Under review - Side-channel communication based on leakage current
Abstract
Laptops perform an indispensable role in our daily learning, work and entertainment due to the convenience. As one of the most essential functions, the importance of com- munication cannot be underestimated. Communication methods based on bypass signals of laptops offer a cost-effective and convenient solution. In this study, we propose an interesting and easily deployable communication method that utilizes the leakage current of a laptop with a metal casing. The proposed scheme, called LeakComm, uses the CPU to modulate the leakage current of the laptop. An earphone or electrode is used to collect the leakage current flowing through the human body and transmit it to the target device for decoding. The modulation and decoding of the leakage current utilizes techniques such as amplitude modulation, spectral subtraction, channel estimation and retransmission mechanism. The proposed scheme enables communication between laptops and other computers, and is more secure than other communication methods based on bypass signals. Experiments in a real-world environment show that two prototypes based on the earphone and electrode achieve the throughputs of approximately 19.76bps and 19.83bps.
Contents
Background
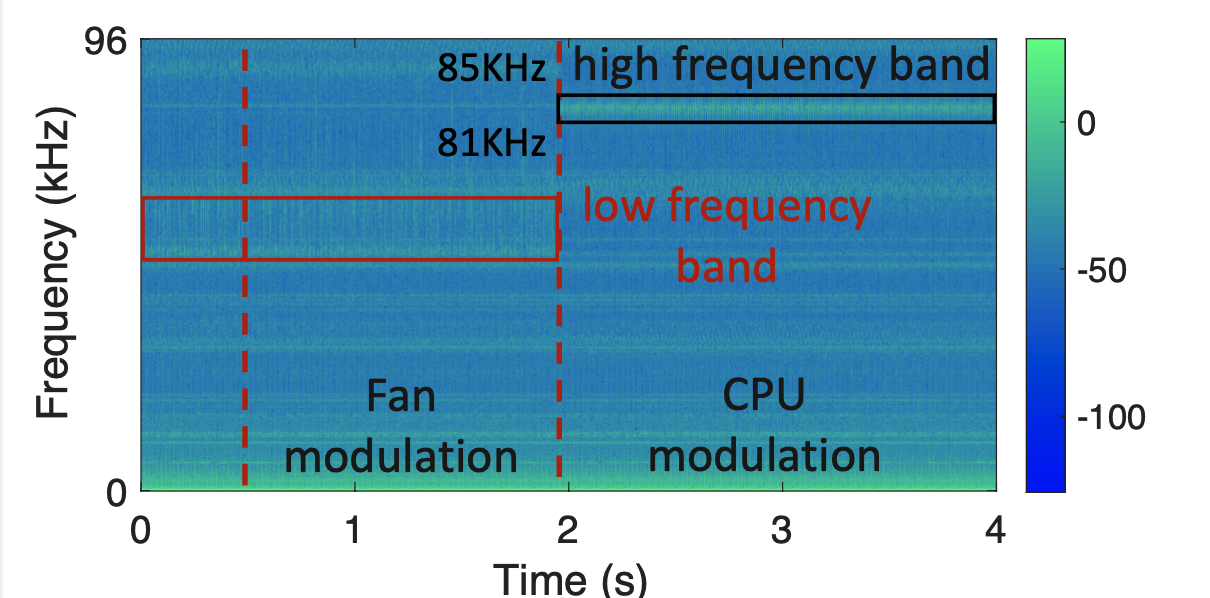
As the leakage current is related to the working state of the laptop [1], we try to control the electronic units of the laptop (e.g. CPU, electronic fan, etc.) to modulate it. We modulated the fan and CPU separately and the leakage currents collected by the earphone and the electrode are shown in Fig. 1, we calculated the spectrogram of the leakage current using Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT). In the preliminary experiments, we set the sampling rate of sound card and AD2 at 192K H z in order to extent the bandwidth. We first increased the power consumption of the laptop fan and then the CPU. It can be seen that the leakage current is significantly enhanced when modulating the CPU to high power consumption; whereas modulating the fan has a negligible effect on the leakage current.
Therefore, we chose to modulate the CPU to verify the feasibility of communication based on leakage current. The advantage of using the CPU is that the CPU can be easily controlled by loop and sleep commands, which are available for most programming languages and operating systems. In addition, it is easy to monitor CPU usage in real time in order to estimate channel conditions.
 |
System
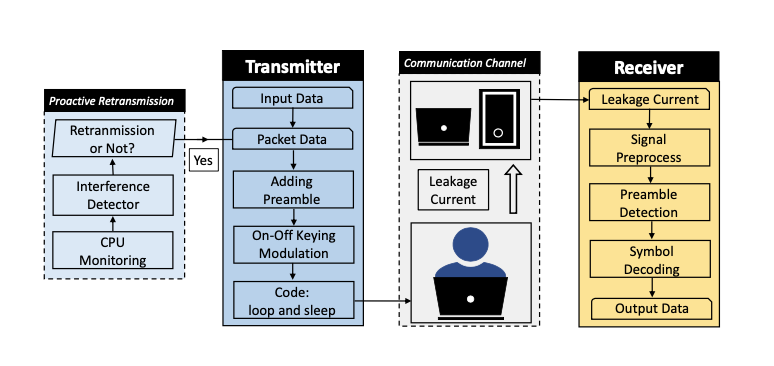
Transmitter
Controlling the operating and idle states of the CPU can vary the power consumption of the CPU, thus enabling modulation of the leakage current. We illustrate the modulation of data bits based on leakage current in the transmitter and introduce the retransmission mechanism to achieve reliable transmission under the noise caused by other applications. The transmitter includes three main parts: preamble design, signal modulation and proactive retransmission.
Receiver
The receiver performs preamble detection for synchronization and signal strength estimation. The signal is also preprocessed and demodulated to extract the data bits. The receiver includes signal preprocessing and decoding.
Evaluation
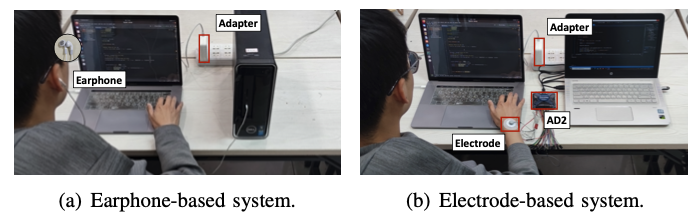
The prototype of LeakComm is adopted on a laptop (MacBook pro) as a transmitter as shown in Fig. 3. The laptop is placed on the desk, and we have to keep the transmitter (Mac- Book pro) on charge.
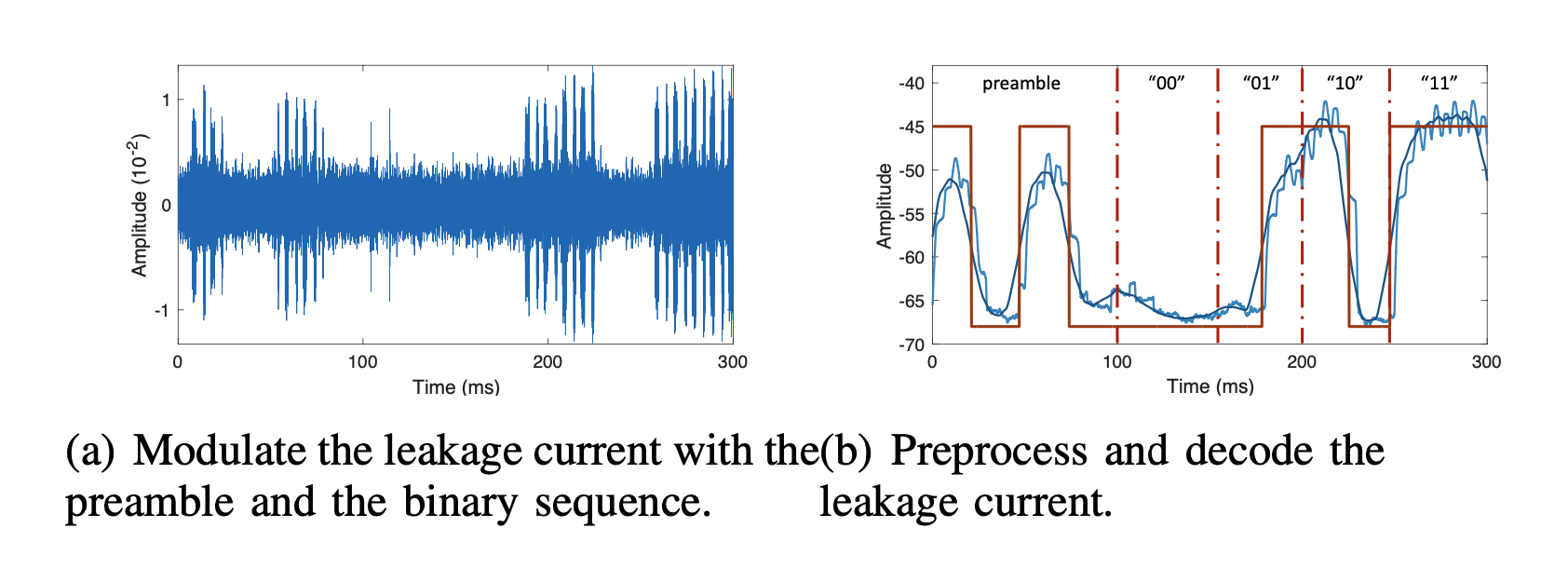
Reference
[1]. W. Meng, “Touch current analysis for power supplies designed for energy efficient regulations,” in 2011 IEEE Symposium on Product Compliance Engineering Proceedings, 2011, pp. 1–6.